+Collections
+nutrition articles
Find out how nutrition can affect your horse's health.
+stockists
A select number of retailers around the country carry our products - you can find them here.
Joint Relief
$215.00
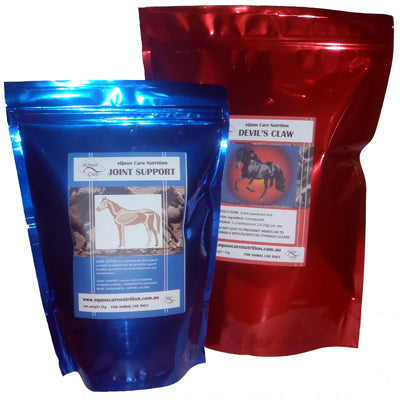
- Does your horse have a joint injury, joint inflammation or arthritis? Combine two of our powerful supplements to support joint recovery and pain management. Joint Support provides key nutrients and nutraceuticals needed to support the body as it builds and repairs joint tissue, whilst Devil's Claw is a natural herb well known for its anti-inflammatory and pain relieving properties.
-
100% pure Devil's Claw root powder
 The Devil's Claw plant (Harpagophytum procumbens) is a native of South Africa, used for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. The active ingredient of Devil's Claw is harpagoside, found in the roots and tubers. Its effectiveness has been found to be comparable with that of cortisone and phenylbutazone. Animal studies suggest that Devil's Claw can help fight inflammation, whilst human trials have seen a reduction in pain, and improved function in people suffering with osteoarthritis and back and neck pain.
The Devil's Claw plant (Harpagophytum procumbens) is a native of South Africa, used for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. The active ingredient of Devil's Claw is harpagoside, found in the roots and tubers. Its effectiveness has been found to be comparable with that of cortisone and phenylbutazone. Animal studies suggest that Devil's Claw can help fight inflammation, whilst human trials have seen a reduction in pain, and improved function in people suffering with osteoarthritis and back and neck pain.Joint Support:
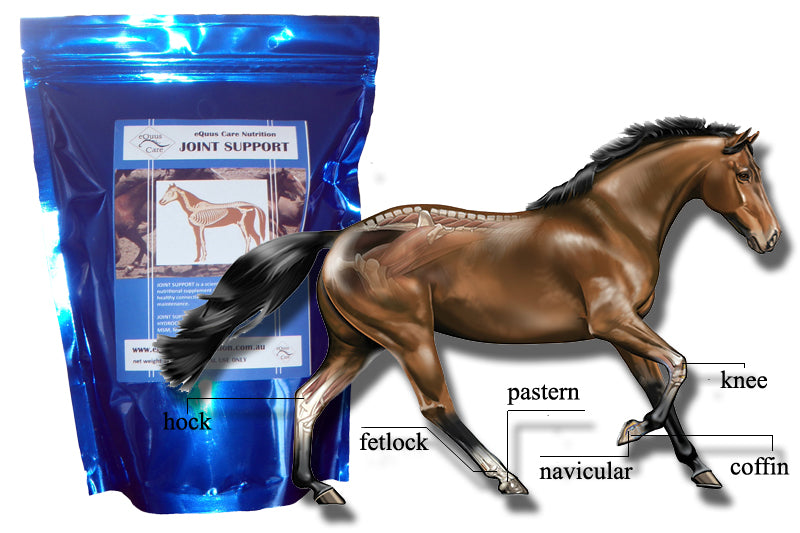
CHONDROITIN SULPHATE is a structural component of joint cartilage. The structure of chondroitin sulphate in cartilage gives cartilage much of its compression resistance, providing shock absorption within the joint. Loss of chondroitin sulphate in cartilage may lead to osteoarthritis.
GLUCOSAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE forms the backbone of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), the building blocks of cartilage and other connective tissue.
MSM is a source of the mineral sulphur, required for the formation of cross-bridges between collagen molecules. These add strength and stability to the structure of collagen rich ligaments, tendons and joint tissues. Glucosamine functions better when there is an adequate source of sulphur.
MANGANESE is a trace mineral that is required by the body for the production of chondroitin sulphates, important in maintaining normal joint cartilage and repairing cartilage. Dietary deficiencies of manganese may result in the abnormal development of bones and joints, and impaired ability to make and repair joint cartilage.
COPPER is a trace mineral which is required for the production of normal connective tissue, including tendons, ligaments and cartilage joint lining. Copper deficiency has been indicated in developmental bone disease, including osteochondrosis dessicans. Dietary deficiency of copper may result in bone and joint disease, and tendon and ligament problems.
ZINC is a trace mineral needed in bone and joint health. Zinc is part of antioxident enzymes in the body which neutralise free radicals before they can damage normal body tissue. -
Joint Support: One level scoop (30g) treats a 500kg horse. Adjust the amount given based on the weight of the horse or pony.
For foals, miniatures and small ponies please download our 'Supplementation Guide for Ponies and Miniatures'Devil's Claw: 10-20g per day. Do not give to pregnant mares, or horses with suspected stomach ulcers.
- We would love to hear your feedback on this product. Drop us a line here:
-
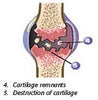
Glucosamine, Chondroitin Sulphate and Equine Osteoarthritis
Recent research suggests that "supplemental glucosamine or chondroitin sulphate may help to prevent cartilage degeneration and treat OA (osteoarthritis)" > read more
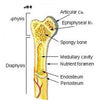
Developmental Orthopaedic Disease: Physitis
In an attempt to meet specific demands, load-bearing structures have faltered and suffered accordingly. Hence, we are now presented with an array of anatomical problems that require investigation. > read more
What is OCD?
OCD, or Osteochondritis Dissecans is a developmental orthopaedic disease that is relatively common, and can affect any horse breed. > read more

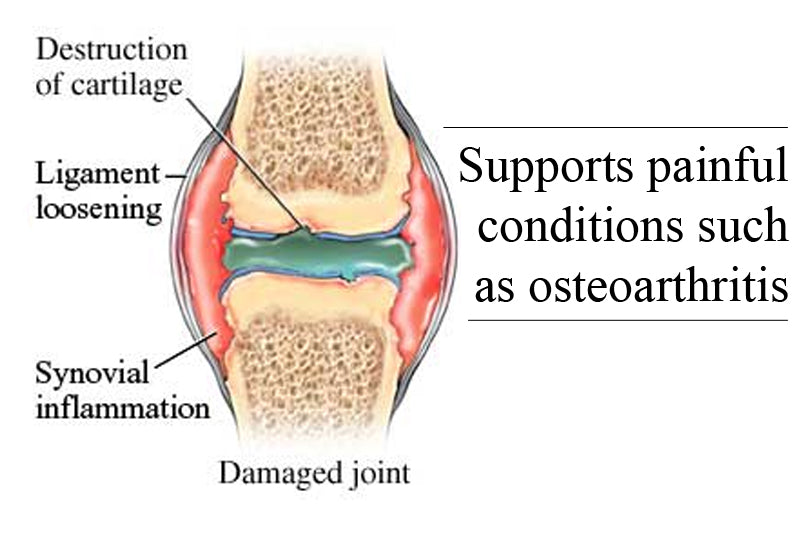
3 big hitters in the fight against osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a chronic condition in which there is progressive degeneration of one or more joints. Symptoms include joint swelling, pain, instability, restrictions in movement and functional impairment. > read more
Share:


 The Devil's Claw plant (Harpagophytum procumbens) is a native of South Africa, used for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. The active ingredient of Devil's Claw is harpagoside, found in the roots and tubers. Its effectiveness has been found to be comparable with that of cortisone and phenylbutazone. Animal studies suggest that Devil's Claw can help fight inflammation, whilst human trials have seen a reduction in pain, and improved function in people suffering with osteoarthritis and back and neck pain.
The Devil's Claw plant (Harpagophytum procumbens) is a native of South Africa, used for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. The active ingredient of Devil's Claw is harpagoside, found in the roots and tubers. Its effectiveness has been found to be comparable with that of cortisone and phenylbutazone. Animal studies suggest that Devil's Claw can help fight inflammation, whilst human trials have seen a reduction in pain, and improved function in people suffering with osteoarthritis and back and neck pain.


